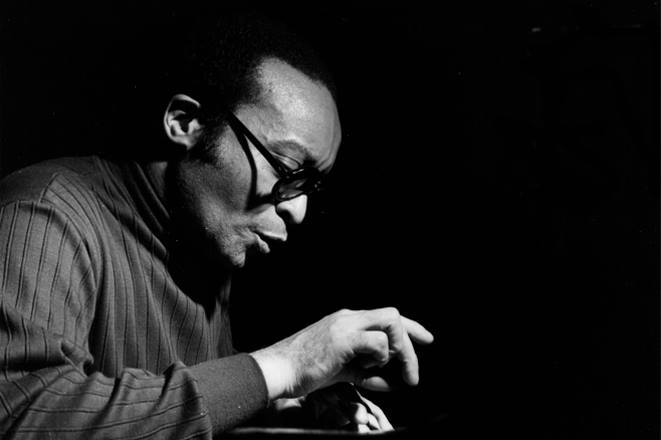
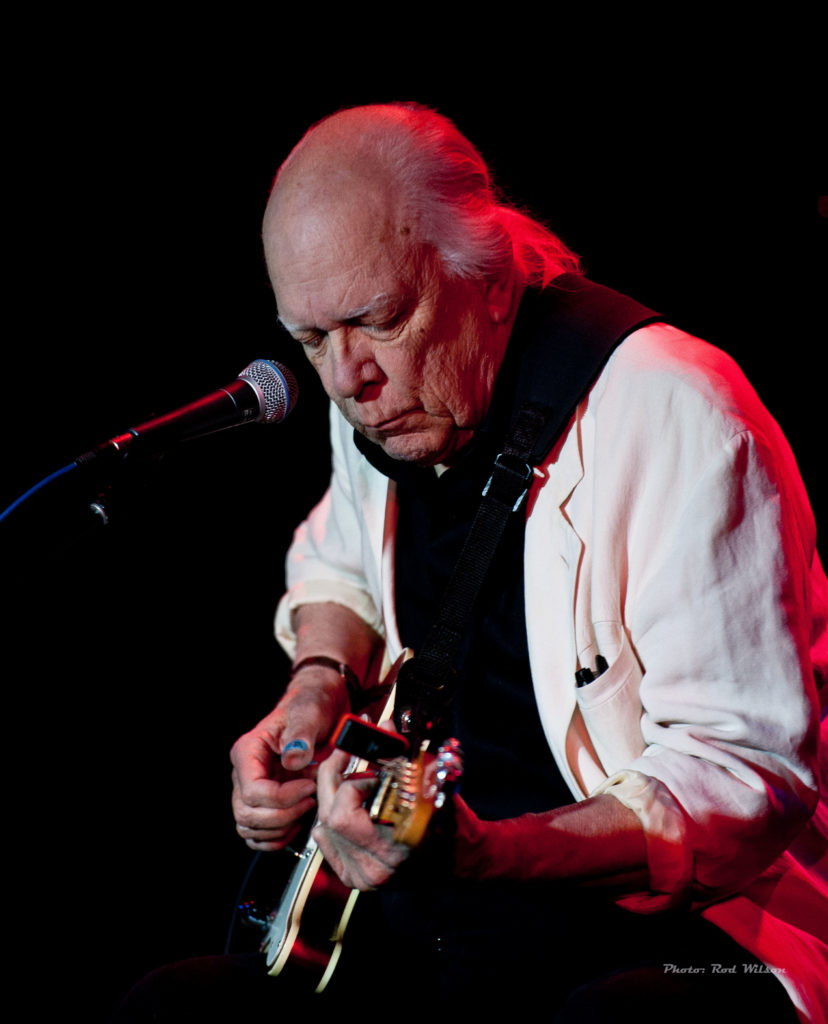
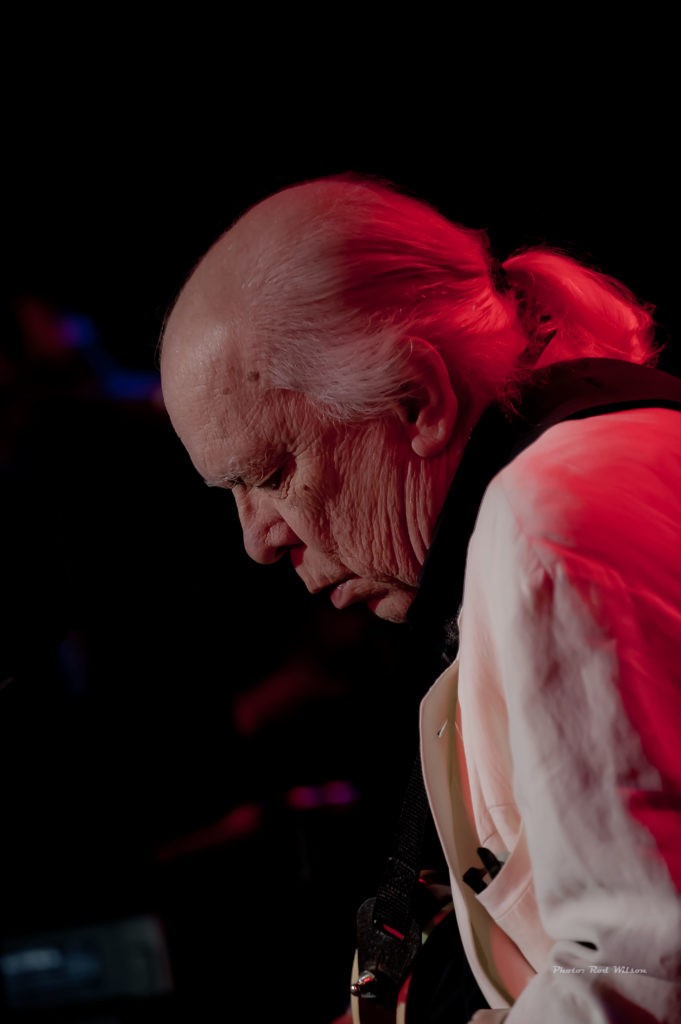
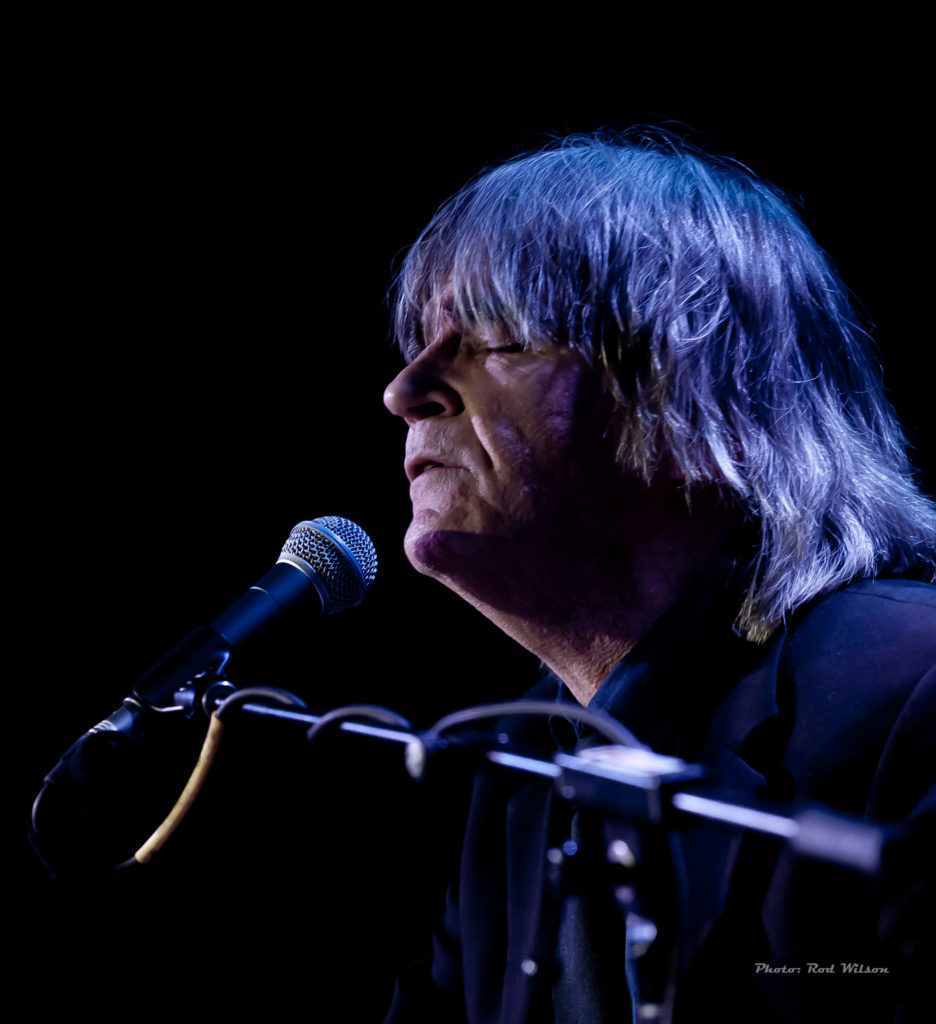
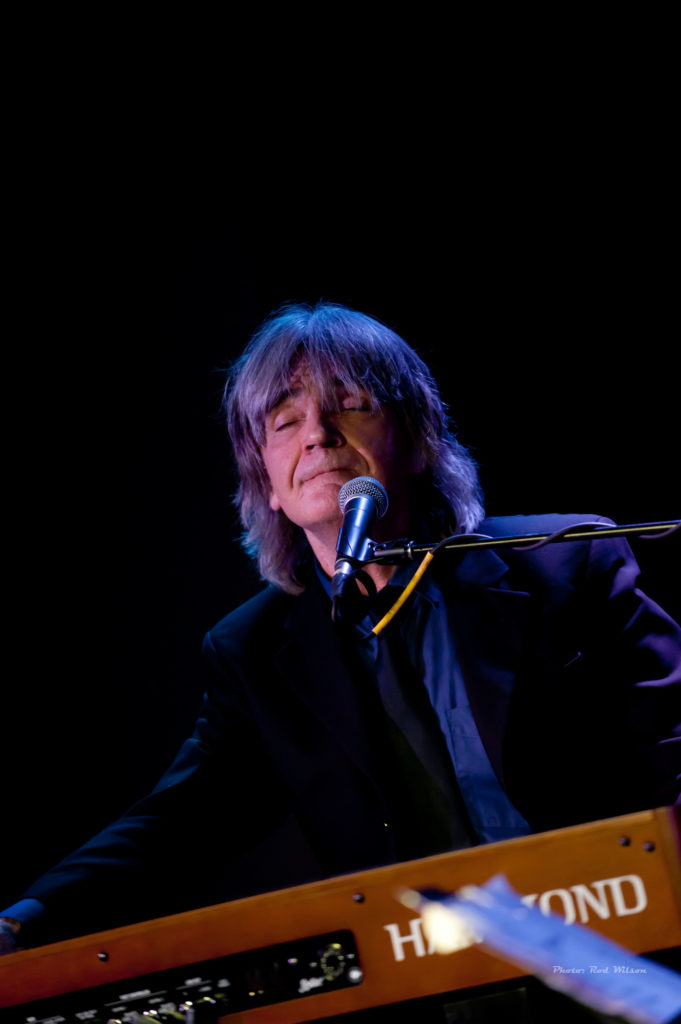
At a concert during the the last European tour of the Miles Davis / John Coltrane Quintet in 1960 a lady in one audience stood up during a John Coltrane solo and pleaded “please make him stop”. I am sure that would be the reaction of most audiences to the music of Cecil Taylor. Even in Jazz circles Cecil Percival Taylor (March 25, 1929 – April 5, 2018) is not exactly a household name. He was a classically trained American pianist and poet and is generally acknowledged as one of the pioneers of the Free Jazz movement. His music is characterized by an extremely energetic, physical approach, resulting in complex improvised sounds that frequently involve tone clusters and polyrhythms. His piano technique has been likened to percussion – referring to the number of keys on a standard piano as “eighty eight tuned drums”. He has also been described as like “Art Tatum with contemporary classical leaning”. The Canadian classical pianist Glenn Gould has been reported as saying “Cecil Taylor is the future of piano music”. It is an interesting comment from a musician who is famous for his precise interpretations of the music of Bach. Taylor is from the opposite end of the musical spectrum. Gould’s interpretations are architectual musical masterpieces while Taylor’s musical musings are more like splashes of molten lava.
Taylor is outside the orderly progression of jazz piano styles of the past century. The normal historical flow of American piano music goes back to the almost classical formalism of Louis Moreau Gottschalk, Scott Joplin, Jelly Roll Morton, and then onto the improvisational styles of James P. Johnson, Earl Hines, “Fats” Waller, Teddy Wilson, Art Tatum, Nat ‘King” Cole and then the moderns – Bud Powell, Oscar Peterson, Bill Evans, Herbie Hancock, Keith Jarrett etc. Taylor stands way outside that tradition. The only pianist that might claim some connection is the Thelonious Monk and he is better known and appreciated as a composer. Like Monk Taylor’s public appearances were performances in the true meaning of the word – music, poetry, dance. At the center of his art was the dazzling physicality and the percussiveness of his playing — his deep, serene, Ellingtonian chords and hummingbird attacks above middle C — which held true well into his 80s. Classically trained, he valued European music for what he called its qualities of “construction” — form, timbre, tone color — and incorporated them into his own aesthetic. “I am not afraid of European influences,” he told the critic Nat Hentoff. “The point is to use them, as Ellington did, as part of my life as an American Negro.” In a long assessment of Mr. Taylor’s work — one of the first — from “Four Lives in the Bebop Business,” a collection of essays on jazz musicians published in 1966, the poet and critic A. B. Spellman wrote: “There is only one musician who has, by general agreement even among those who have disliked his music, been able to incorporate all that he wants to take from classical and modern Western composition into his own distinctly individual kind of blues without in the least compromising those blues, and that is Cecil Taylor, a kind of Bartok in reverse.” Because his fully formed work was not folkish or pop-oriented, did not swing consistently (often it did not swing at all) and never entered the consensual jazz repertoire, Mr. Taylor could be understood to occupy an isolated place. Even after he was rewarded and lionized his music has not been easy to quantify. If improvisation means using intuition and risk in the present moment, there have been few musicians who took that challenge more seriously than Mr. Taylor. If one of his phrases seemed of paramount importance, another such phrase generally arrived right behind it. The range of expression in his keyboard touch encompassed caresses, rumbles and crashes. – (excepts from Wikipedia).
Taylor may not have had a big following but he was not without honors during his lifetime. Even after he was rewarded and lionized — he was given a Guggenheim fellowship in 1973, a National Endowment for the Arts Jazz Masters award in 1990, a MacArthur fellowship in 1991 and the Kyoto Prize in 2014 — his music was not easy to quantify nor did it have a great following. There was no academy for what Cecil Taylor did, and partly for that reason he became one himself, teaching for stretches in the 1970s at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and at Antioch College in Ohio. (He was given an honorary doctorate by the New England Conservatory in 1977.) Not until the mid-1970s, Mr. Lyons told the writer John Litweiler, did The Cecil Taylor Unit have enough work so that member musicians could make a living from it — mostly in Europe. Although classically trained his comment on written music bears repeating – “When you think about musicians who are reading music,” he said in “All the Notes,” a 1993 documentary directed by Chris Felver, “my contention has always been: The energy that you’re using deciphering what the symbol is, is taking away from the maximum creative energy that you might have had if you understood that it’s but a symbol.” (excepts from Wikipedia). I agree with the comment but most of us mere mortals have to start somewhere and once the music is under your belt then perhaps the written symbols should be discarded.
In some ways he reminds me of Frank Zappa. Frank was a “rock” musician who was very distinctly outside the traditions of Rock and Roll. Just try and jam along with a Frank Zappa recording and I think you will get my meaning.
@@@@@@@@@@@@
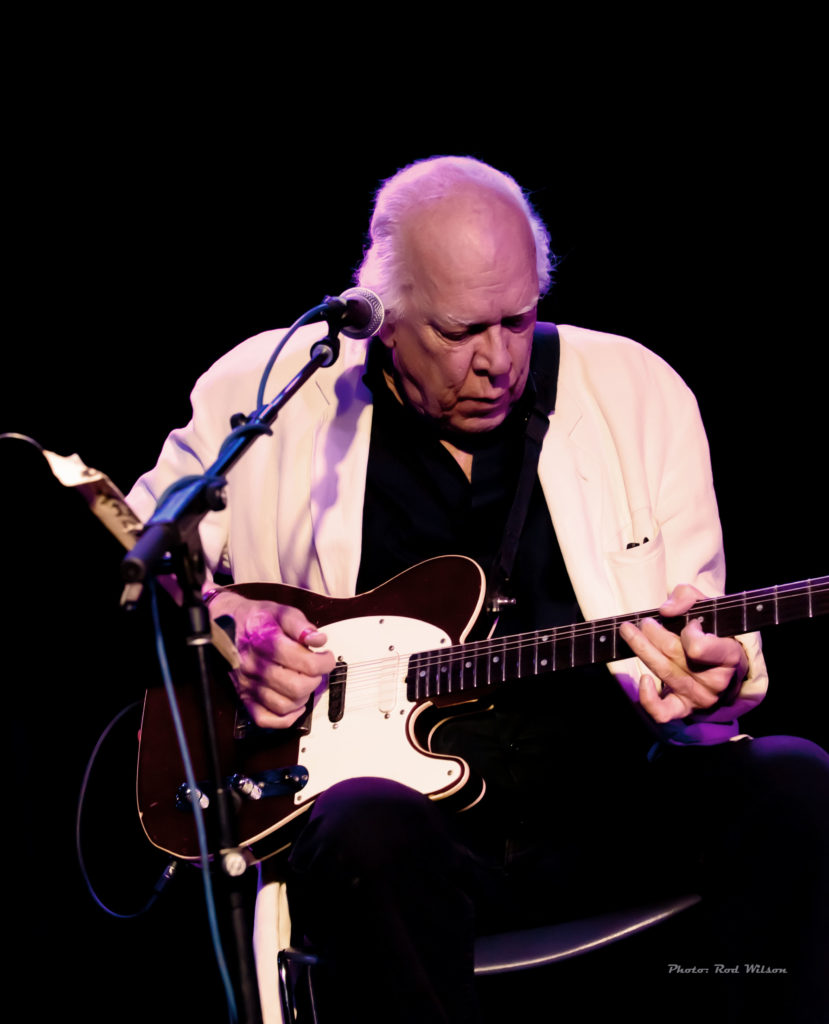
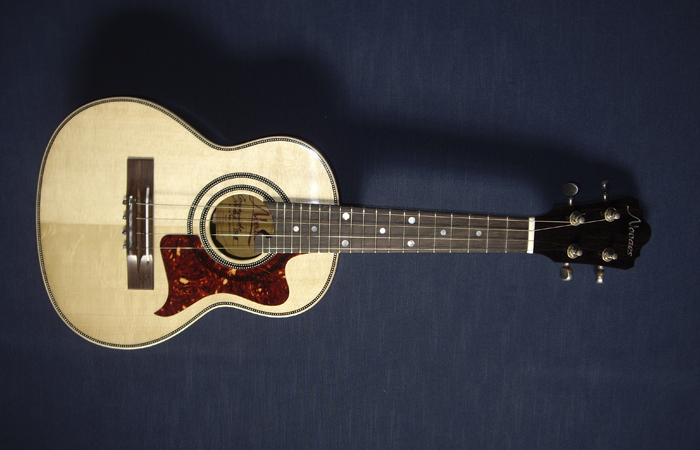

















 Basically, that is an an open G tuning, a octave higher but almost identical, to the top four strings of the acoustic guitar. The difference is that the top string on the Cavaquinho is tuned down to D. Speaking from experience it was tempting to just tune the guitar like a Cavaquinho and play it as such. It was good idea at the time but basically it doesn’t work. The Cavaquinho has a very short scale length and the normal Cavaquinho Choro stretches from
Basically, that is an an open G tuning, a octave higher but almost identical, to the top four strings of the acoustic guitar. The difference is that the top string on the Cavaquinho is tuned down to D. Speaking from experience it was tempting to just tune the guitar like a Cavaquinho and play it as such. It was good idea at the time but basically it doesn’t work. The Cavaquinho has a very short scale length and the normal Cavaquinho Choro stretches from  the 1st and 2nd to seventh fret are dam near impossible on the guitar. Beside it does not have the nice high traditional Cavaquinho sound. D’Addario manufactures stainless steel ball end strings (EJ93, gauges 11-13-23w-28w) specifically for the Cavaquinho and are available from a number of on line sites. It is unlikely you will find them in your local music store. The Godin instrument is equipped with their signature on-board electronics that is virtually free of feed back. In that regard, and in other manufacturing details, the Godin Cavaquinho is similar to their acoustic and semi-acoustic Nylon Classical, Multi Oud and Seven String Guitars.
the 1st and 2nd to seventh fret are dam near impossible on the guitar. Beside it does not have the nice high traditional Cavaquinho sound. D’Addario manufactures stainless steel ball end strings (EJ93, gauges 11-13-23w-28w) specifically for the Cavaquinho and are available from a number of on line sites. It is unlikely you will find them in your local music store. The Godin instrument is equipped with their signature on-board electronics that is virtually free of feed back. In that regard, and in other manufacturing details, the Godin Cavaquinho is similar to their acoustic and semi-acoustic Nylon Classical, Multi Oud and Seven String Guitars.
 Sunday January 28, 2018 12:30 – 3:30 pm: OPEN MIC AT THE BEAN TREE IN THE KIMBERLEY PLATZL hosted by Bill St Amand
Sunday January 28, 2018 12:30 – 3:30 pm: OPEN MIC AT THE BEAN TREE IN THE KIMBERLEY PLATZL hosted by Bill St Amand